单页面的状态管理
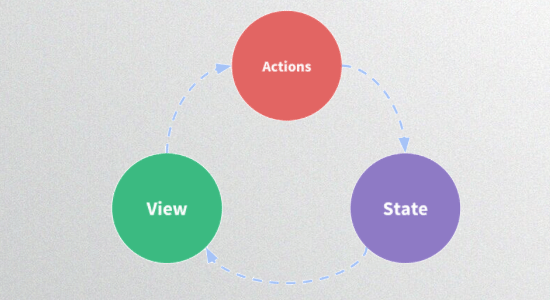 State:状态;
State:状态;
View:视图层,可以针对State的变化显示不同信息;
Actions:主要是用户的各种操作:点击、输入等,会导致State的变化;
多页面的状态管理
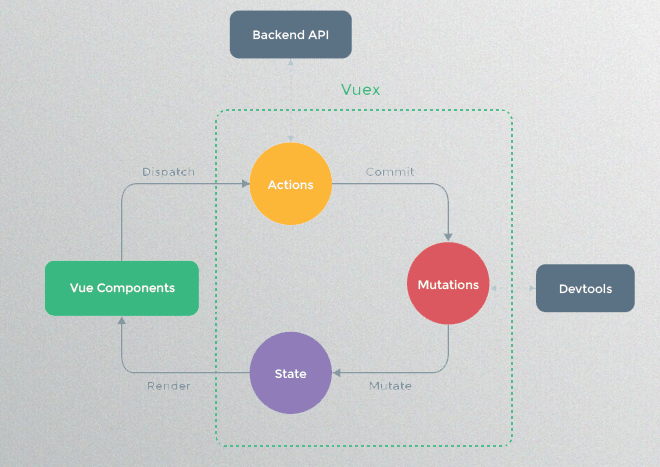
- 多个视图都依赖同一个状态;
- 不同页面的Actions都想修改同一个状态。
全局单例模式:将共享的状态抽取出来,交给vuex进行统一管理;然后每个视图按照规定好的规则,进行访问和修改等操作。
简单使用Vuex
- 提取出一个公共的store对象,用于保存在多个组件中共享的状态;
- 将store对象放置在new Vue对象中,这样可以保证在所有的组件中都可以使用到;
- 在其他组件中使用store对象中保存的状态:
a. 通过
this.$store.state属性来访问状态
b. 通过this.$store.commit('mutation中的方法')来修改状态
eg:在项目中src文件下新建store文件,然后在store文件中新建一个__.js文件;通过npm install Vuex -S安装vuex,在main.js文件上导入:import store from './store';然后在store文件上的__.js文件上导入Vue和Vuex:import Vue from 'vue'和import Vuex from 'vuex',然后在使用Vue.use(Vuex),最后创建实例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
var store = bew Vuex.useStore({
state:{},
mutations:{},
actions:{},
getters:{},
modules:{}
})
一、getters
getters相当于计算属性,对state中的数据进行处理如过滤等,并返回新数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
//eg:
getters:{
powCounter(State){//计算state中counter的平方
return state.counter * state.counter
},
}
//然后在其他组件中{ { $store.getters.powCounter } }
然后在其他组件中{ { $store.getters.powCounter } }
getters作为参数和传递参数
例如上例中如果要计算counter的三次方
1
2
3
newCounter(State, getters){
return getter.powCounter * state.counter
}
利用mapGetters辅助函数将getter映射到局部计算属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
//eg:
import {mapGetters} from 'vuex'
//方法一:使用对象展开运算符,将getter混入computed对象中
computed:{...mapGetters(['cartLength', '...',...])}
//方法二:将getter属性另取一个名字,使用对象形式:
computed:{...mapGetters({len:'cartLength', ...})}
二、mutations
vuex的state的更新唯一方式:提交mutation
mutation主要包括两部分:
- 字符串的事件类型;
- 一个回调函数,该回调函数的第一个参数为state
mutation的定义方式:
1
2
3
4
5
6
//eg:
mutation:{
add(state){
state.count++
}
}
在组件methods中通过mutation更新:
1
2
3
add(){
this.$store.commit('add)
}
mutation传参
参数被称为是mutation的载荷(payload)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
//eg:
decrement(state,n){
state.count -= n
}
decrement(){
this.$store.commit('decrement', 2)
}
如果参数不唯一,可以通过对象的形式传递,然后可以从对象中取相关信息eg: obj.对象中的属性名
mutation提交风格
- 普通:
this.$store.commit('addCount', count) - 特殊:
1 2 3 4
this.$store.commit({ type:'addCount', count:count })
特殊风格中mutation上的处理方式是将整个commit的对象作为payload使用
1
2
3
4
//eg:
addCount(state, payload){//此处payload是一个对象
state.count = payload.count
}
响应式方法:
Vue.set(修改的东西, string/number, '值')eg:Vue.set(state.info, 'sex', 'fame')Vue.delete( , )
Vuex要求mutation中的方法必须是同步方法,如果是异步操作,devtools将不能追踪这个操作的变化
三、Action
Action类似于mutation,可以用来替代mutation进行异步操作(即异步操作时,先在methods中dispatch给action,然后action再commit给mutation)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
//eg:组件中的methods的方法
update(){
this.$store.dispatch('actionUpdate')
}
//action中的异步操作:
actionUpdate(context){
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('update')
},1000)
}
//mutation中的方法:
update(state){
Vue.set(state.person, 'name', 'Martin')
}
四、module
当应用变得复杂时,store对象就有可能变得相当臃肿,这时,Vuex允许将store分割成模块(Module),而每个模块拥有自己的store、mutations、actions、getters等